I first wrote CyberPipe when I was on the front lines of incident response, driven by the need for more robust and efficient triage collections, whether online or off. Over the years, CyberPipe continues to adapt and improve, addressing the ever-changing challenges faced by incident response practitioners.
CyberPipe (formerly CSIRT-Collect) is a PowerShell script that is designed to streamline the collection of digital evidence using Magnet Response in enterprise environments, ensuring that responders can gather critical data efficiently and effectively. Other features include detection of encrypted drives, BitLocker key recovery, and memory image collection.
The most recent update includes enhancements in three areas: Collection, Capabilities, and Reliability.
🔍 What’s New in 5.2
Intelligent Collection
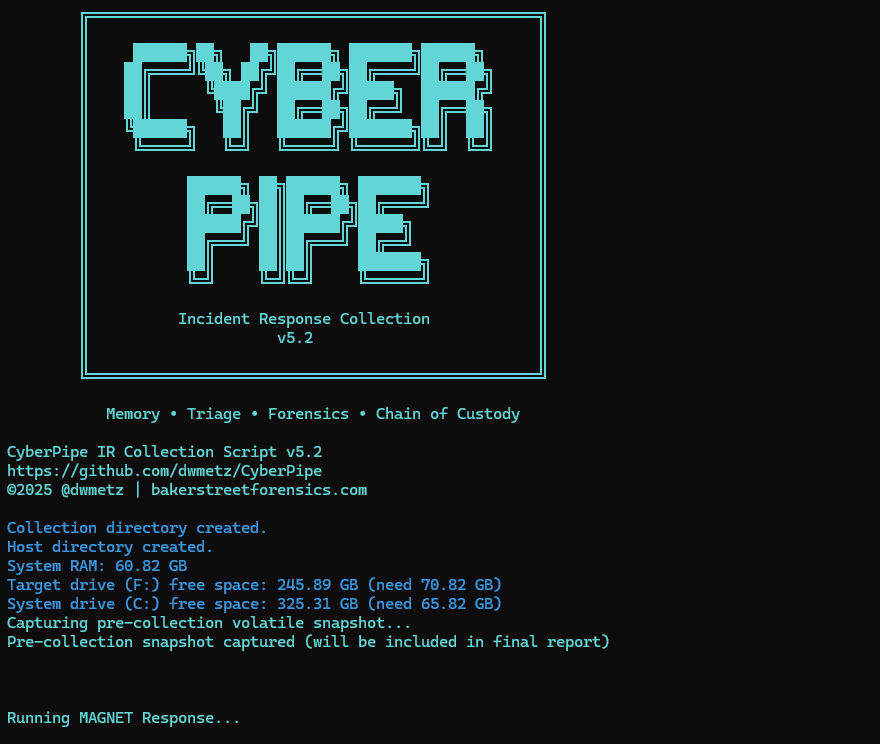
- The script now includes dual disk space validation, checking both the target drive and the system drive with profile-aware thresholds to prevent sudden failures due to insufficient space.
- A pre-collection volatile snapshot captures uptime, users, connections, and processes to preserve transient state before heavy operations begin.
- Reports virtual environment detection (VMware, Hyper-V, VirtualBox, etc.) to help analysts understand collection limitations.
- Real-time progress indicators provide accurate size tracking during the collection, offering responders visibility into the remaining data capture.
Enhanced Capabilities
- The new QuickTriage profile allows for rapid collection of volatile and system artifacts when time is ticking.
- BitLocker recovery now includes all volumes, not just the C: drive.
- A single-file report (CyberPipe-Report.txt) consolidates metadata and a summary of collected artifacts in a human-readable format.
- All collected artifacts and logs are hashed using SHA-256 to enhance integrity and chain of custody.
- Output compression is available via the -Compress flag, aiding in storage and transfer.
- Network collection is simplified with the -Net parameter, eliminating the need for manual network path or configuration edits.
Improved Reliability
- Profile-aware space checks alert when free space is insufficient for a chosen profile, preventing silent failures.
- The script now validates exit codes from MAGNET Response to detect failures more effectively.
- Artifact verification after collection ensures that all expected items were gathered.
- Error handling and messaging have been refined to provide clearer feedback to the operator.
What I’m hoping this delivers
CyberPipe 5.2 aims to address some challenges observed in real-world triage and live-response operations:
- Resilience in constrained environments — dual drive checks and profile awareness help prevent mid-collection failures.
- Better transparency and oversight — real-time progress display and post-collection verification enhance confidence.
- Faster response options — the QuickTriage profile is suitable when speed is paramount.
- Stronger forensic hygiene — SHA-256 hashing, improved error detection, and full-volume BitLocker key recovery contribute to defensibility.
- Easier network deployments — built-in ‘-Net‘ support facilitates smoother remote collection.
As always, CyberPipe is freely available at https://github.com/dwmetz/CyberPipe. Forks and Contributions welcome and appreciated.
Is there a feature you’d like to see? I think next I might work on support for copying output to AWS/Azure. Thoughts?